Click here for English pdf of the Declaration of Statement on Scientific Temper with signatories
Other languages: Tamil Bengali Telugu
Click here for English pdf of the Resolution adopted along with the Declaration on Scientific Temper
Other languages: Tamil Bengali
Leaflet/Powerpoint distributed about the Declaration/Resolution in Tamil Bengali
Adopted at “Campaign for scientific temper culmination program and National convention for declaration on scientific temper”
held on 28th Feb 2024 at Kolkata
Statement on Scientific Temper in the Current Context
Executive Summary There is an urgent need for a renewed commitment to evidence-based reasoning, critical thinking and a scientific approach in India, especially amidst growing socio-political movements that challenge a scientific temper and universal knowledge production based on commonly agreed methods and understanding. Given the changes in society and technology since the earlier declarations on scientific temper in 1981 and 2011, we emphasise the importance of embracing natural and social sciences, humanities, and the rational experiences of ordinary people in the common endeavour to combat the post-truth culture, the intentional promotion of ignorance, and diminishing trust in science exacerbated by misuse of technology. We call for action across three fronts: the State’s role, the involvement of scientific and academic institutions, and combating the undermining of science by the State, the erosion of academic freedom, and the spread of pseudo-science and unscientific beliefs. We urge scientists, intellectuals, and other like-minded individuals to support evidence-based thinking and policy-making and to uphold constitutional values to foster a scientific temper.
Introduction Since the Coonoor Statement on Scientific Temper in 1981 and the Palampur Declaration in 2011, there have been significant socio-political changes in India and around the world. Briefly, these earlier statements had emphasised the importance of fostering a scientific attitude among the people for development and social advancement. Over time, movements promoting scientific temper in India have also evolved in accordance with changing public perceptions of science and technology (S&T).
Recently, new challenges have emerged in India and elsewhere in the world in the form of strong socio-political movements, backed by the State power, that seek to oppose any scientific approach, evidence-based reasoning or, indeed, any perspective that acknowledges universal scientific knowledge. Globally, a post-truth culture is spreading, marked by a deliberate spreading of ignorance and an anti-intellectual atmosphere, along with a diminishing trust in science. It is ironic that technology, part of the broad umbrella of science, is being harnessed to support these trends through social media, such that manufactured sentiment, prejudice, false narratives, baseless opinions and conspiracy theories gain acceptance as valid ways of thinking.
Against this background, the current situation requires a renewed commitment to robust evidence-based reasoning, drawing from accumulated knowledge in the natural and social sciences, and humanities, as well as from the know-how and rational experiences of working people. Such reasoning aligns with well-recognized methodologies of different disciplines, including emerging interdisciplinary research, applicable not only in academic environments, but also in public discourse and understanding. Both scientists and lay practitioners need to actively embrace and popularise these methods considering the new socio-political realities in India.
This contemporary statement on Scientific Temper has become essential, to address present challenges. This statement shall not undertake a critical review of the previous statements / declarations or debate their points. Instead, it acknowledges past debates and critiques, incorporating their essence into the current statement, recognizing the commonality of scientific disciplines and their methodologies. Rather than revisiting old debates, the focus here is on delineating the significant challenges faced in contemporary India for the constitutionally mandated task of promoting scientific temper, the spirit of inquiry, and humanism. Knowledge production and advancement through purposeful discovery and evidence-based reasoning, including thorough consideration of diverse opinions, is currently under severe threat both in academia and in society at large.
Dangerous new theatre As noted earlier, the arena for fostering scientific temper has evolved significantly in recent decades, becoming increasingly contested, including aggressive socio-cultural forces as well as governmental policies and administrative measures antagonistic to scientific temper. The current situation in India demands critical understanding and action on three interrelated fronts: the role of the State and polity, the character and function of scientific research and academic institutions, and malign influences in society and among the general public.
Article 51A(h) of the Constitution of India speaks of the duty of citizens to promote scientific temper. There is concern in some quarters that responsibilities of the State in this regard have not been adequately highlighted. While it might have been assumed that the State’s primary responsibility is implicit when citizens are called upon for certain duties, there is a need for a clearer delineation of the State’s role.
Note: In the declaration, the terms ‘scientists’ and ‘scientific institutions’ are used as terms denoting all natural sciences, social sciences and humanities disciplines, and those others following an evidence-based path of knowledge production and understanding.
Role of the State In the initial post-Independence decades, the Indian State placed significant trust in scientists1 and scientific institutions. Development policies were evidence-driven, with research institutions and centres of excellence enjoying high priority and prestige, and enjoying substantial autonomy. Documents like the Industrial Policy Resolution and a unique Scientific Policy Resolution were foundational to planned development, guided by a multidisciplinary group of experts in the Planning Commission. Independent scientists and social scientists, both from India and abroad, were involved in policy-making, underlining the importance given to science and evidence-based policy-making. Notably, religion played a minimal role in state affairs, and secularism, defined as non-discrimination and equal respect for all religions, was practised. However, the evils of casteism and communalism have never been properly eliminated.
However, in subsequent years, bureaucratism, elitism, and a techno-fix mentality crept into the system, creating something of a divide between scientists and the general public. Trust in scientific institutions also eroded as a perception grew that “establishment science” primarily served officialdom and corporate interests, rather than the public good as supported by verifiable data. During this period, academic, professional, and informed activist voices in civil society critiqued official narratives, influencing public opinion and contributing to critical thinking and evidence-based policymaking. While the State may not have proactively cultivated scientific temper, it engaged with and supported activities to popularise science among the wider public and children. The State also provided considerable space in governance and public discourse for non-official scientific, expert, and informed lay opinion.
Undermining science and a scientific approach Presently, the State displays a stark departure from this earlier stance. Government and its various organs now actively oppose a scientific approach, independent or critical thinking, and evidence-based thinking and policy-making. This antagonistic stance is widely and persistently communicated to the public through various means, perpetuating such attitudes. State support for research and development (R&D), already below comparable countries as a percentage of GDP, has hit historic lows, raising serious concerns about India’s future in the knowledge era. Domestic assembly by cheap labour is misrepresented as self-reliance, thus also underplaying the need for research and knowledge production.
Funding, fellowships, and independent research face severe cuts in academic and research institutions, burdened by overpowering bureaucratic structures. Career advancement now favours adherence to dominant ideologies, sycophancy, and obedience to government directives over adherence to imperatives arising from domain expertise and research-based insights. Development data and India’s position in reputed international rankings are contested on spurious grounds. Similar data generated in India, even by government institutions, are rejected or manipulated to fit political narratives. On numerous issues, the government claims to lack data, but still proceeds with policy decisions. Open discussions in higher learning institutions are discouraged, hindering critical thinking, pluralism, and academic freedom.
Beyond image management, these tendencies undermine a scientific approach and evidence-based policymaking, demoralising the knowledge production community and fostering anti-intellectual attitudes.
The State and allied social forces directly undermine science and its methods among the public. Unscientific claims by prominent figures in political circles, boasting of imaginary technological achievements and exaggerated ideas about ancient Indian knowledge, are used to build and support a hyper-nationalist narrative. These assertions lack evidence, relying on ambiguous mythological references and dubious interpretations of ancient texts, often draped in quasi-religious cover so as to suppress dissenting voices. Such fanciful and boastful claims undermine many actual substantial contributions of ancient India emanating from various cultural streams and covering intellectual as well as artisanal and technical accomplishments. Critics of such claims are readily branded as anti-national or westernised, questioning both history and science, and undermining the scientific method. Dissent and plurality of opinion, known to be enabling conditions for intellectual progress, are presently under threat.
Assault on the education sector It is disheartening to witness these trends now being introduced into the formal education system, potentially influencing an entire generation unless effectively countered. School textbooks and readings in higher education are undergoing revisions that promote the idea of the unquestioned superiority of knowledge in ancient India, while downplaying the role of other civilizations and their groundbreaking contributions. Whereas addressing Euro-centrism and acknowledging the contributions from ancient India, China, and other “eastern” civilizations is essential, denying the emergence of modern science and technology and the industrial revolution, and the factors leading to it, is not only untruthful but also misleading. The giant strides of modern science and technology cannot be undermined or replaced by fictional narratives, as seen in revised school textbooks of agencies at the Centre and in various states.
These revised textbooks also omit chapters on crucial historical, societal, economic, and ecological issues in India. In an examination-oriented system not fostering critical thinking, this leaves students ill-prepared for higher studies or research and for their roles as informed citizens contributing to national development.
In higher education, mandatory courses on “traditional knowledge systems” are being introduced, presenting a-historical and distorted accounts of knowledge in ancient India. These courses exclusively glorify the Vedic-Sanskritic tradition, neglecting other cultural streams in ancient India and completely disregarding the significant generation of new knowledge in mediaeval India, out of prejudice against particular religious and cultural
streams. This deliberate slant aims to erase or rewrite historical evidence and obstruct critical thinking, leaving students and citizens vulnerable to bias and instilling a distorted view of syncretic Indian traditions and multicultural reality. In the long run, this will result in incalculable damage to the progress of Indian science and to social harmony.
Societal attack In recent decades, India has witnessed the growth of socio-religious orthodoxy, traditionalism, and revivalism, fueled by majoritarian socio-political forces. Traditional religious practices, festivals, and communal forms of organisation have proliferated. Numerous “Godmen” have emerged with substantial resources, sizable followings, and at times, significant political backing. These cults, despite projecting high-thinking spiritualism, have propagated superstitions, pseudo-scientific beliefs, and socio-religious orthodoxy.
Today, social forces aligned with the ruling establishment and supported by the State, disseminate pseudo-science and a belief in mythology as history. False narratives are being used to construct a unitary majoritarian religion and culture, contrary to the diverse religious beliefs even among the majority community. False and unscientific narratives, such as vegetarianism as a dominant “traditional” practice, are being promoted, contradicting scientific surveys conducted by official agencies.
During the COVID pandemic, superstitions and pseudo-scientific notions related to health were actively promoted under the guise of endorsing “traditional” or ancient Indian health systems while implicitly or explicitly criticising modern medicine. Highly placed authorities encouraged practices like lighting lamps and clanging utensils to ward off the virus, with social media amplifying purported “proof” of efficacy, such as recordings of “cosmic vibrations” by NASA. Other pseudo-scientific claims are similarly backed by false evidence supposedly coming from reputed scientific agencies. Artificial creation of long-lost legendary ancient rivers is being undertaken to perpetuate mythology. All these exploit the enduring respect common people hold for science and its truth value. The forces of unreason seek to sow confusion regarding evidence and scientific methods.
Social media and digital technologies play a pivotal role in the State-backed dissemination of unscientific and anti-scientific views, pseudo-science, false narratives, and conspiracy theories aimed at undermining a scientific approach.
In closing, it is important to address the idea that “other worldly” religious beliefs pose the only or major obstacle to fostering a scientific temper in India. Faith poses many challenges which science or rationalism may not always be able to tackle, insofar as faith itself may be defined or perceived as belonging to a non-physical domain. Freedom of religion or Individual faith may indeed be accorded due recognition. At the same time, discriminatory practices or those that impinge on others’ rights or affect public order, must be opposed, and their irrational basis explained. Obscurantism persists due to ongoing weaknesses in society itself, highlighting larger battles that need to be fought, of which the present one may be just a part. Given the organised challenges to a scientific approach discussed earlier, a more focused and targeted strategy is required for the campaign to promote or strengthen a scientific temper.
Declaration We scientists and intellectuals across disciplines, activists and all individuals passionate about spreading a scientific temper, acknowledge that the struggle to promote a scientific temper is wide-ranging and embraces many dimensions. Yet we also understand that, given the grave threats posed in the current context, the major challenge in this period is to combat and roll back these threats. We realise the imminent danger posed by organised multi-pronged attacks to undermine a scientific attitude among the populace. Such attacks not only disseminate pseudo-science, blind faith, and unreason but also promote obscurantism, communitarian prejudices, and discrimination, striking at the core of a humanist approach. False narratives, unfounded opinions, and a cloak of religiosity are wielded to instil adherence to a manufactured, homogenised, majoritarian idea of India.
We, the signatories of this declaration, re-attest the importance of working towards promotion of scientific temper in society. We recognise the grassroots work put in by people’s science movements, other like-minded organisations and dedicated individuals, and commit to support these and other similar efforts. We appeal to like-minded individuals in academia and research institutions, the bureaucracy, and the political class to take a stand upholding constitutional values.
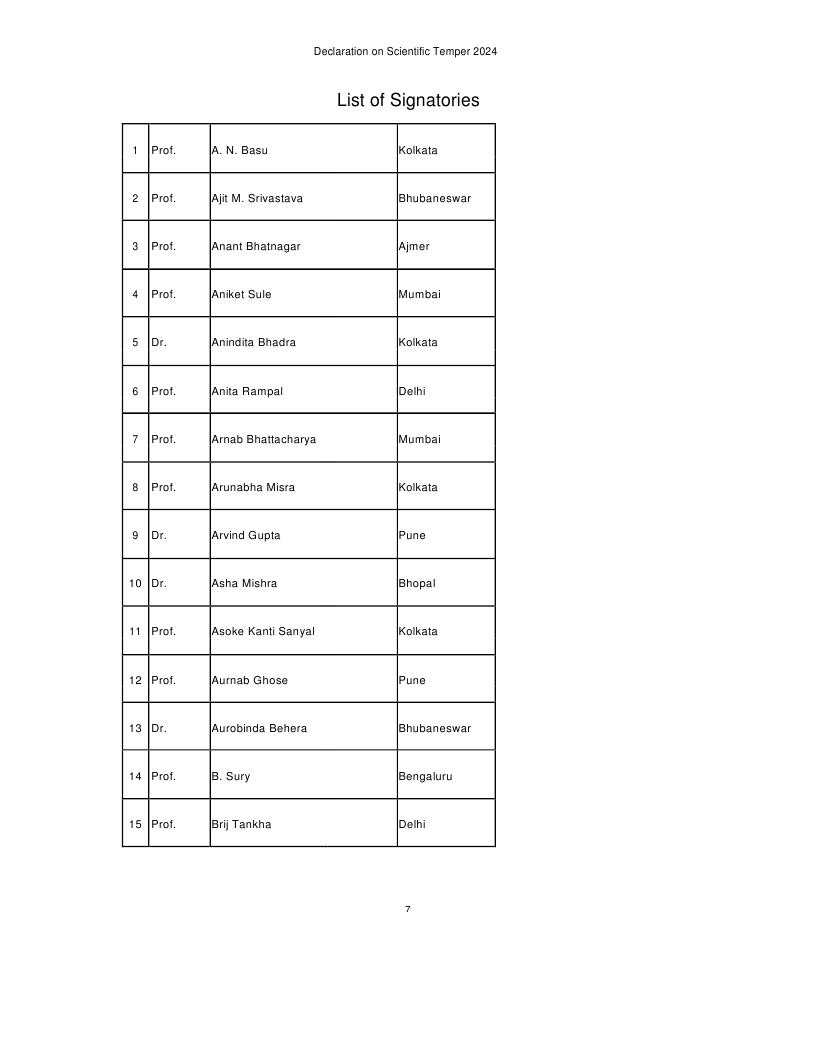
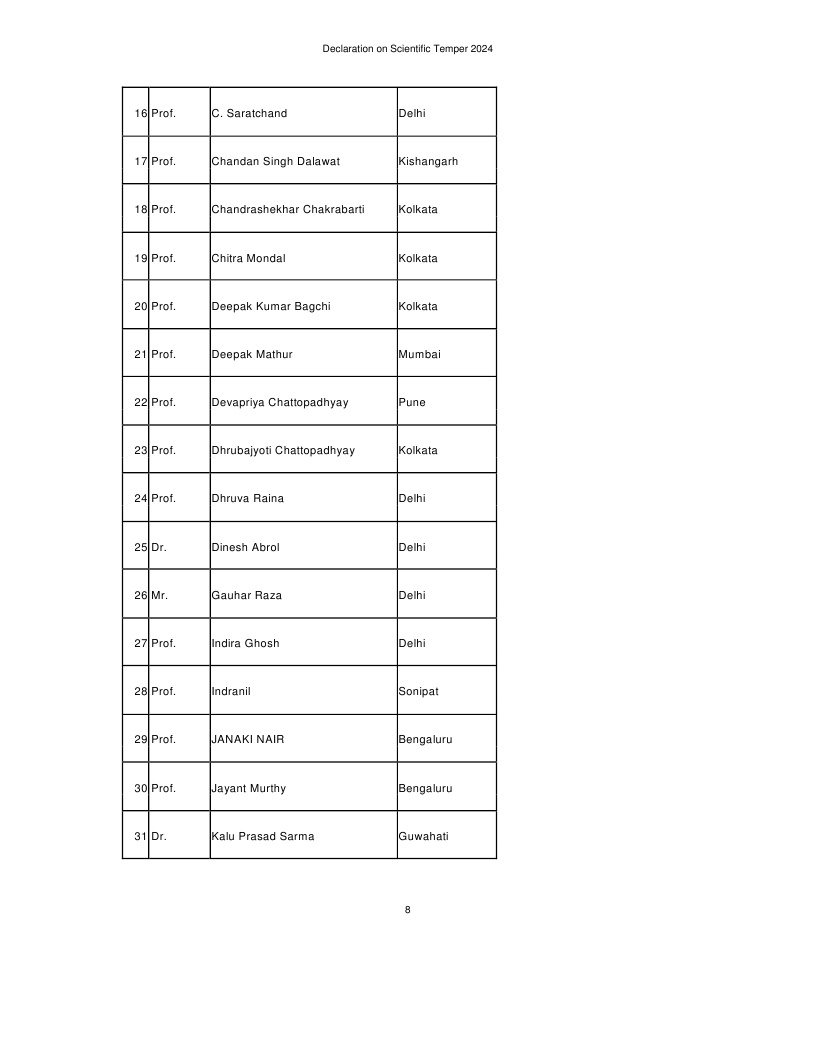
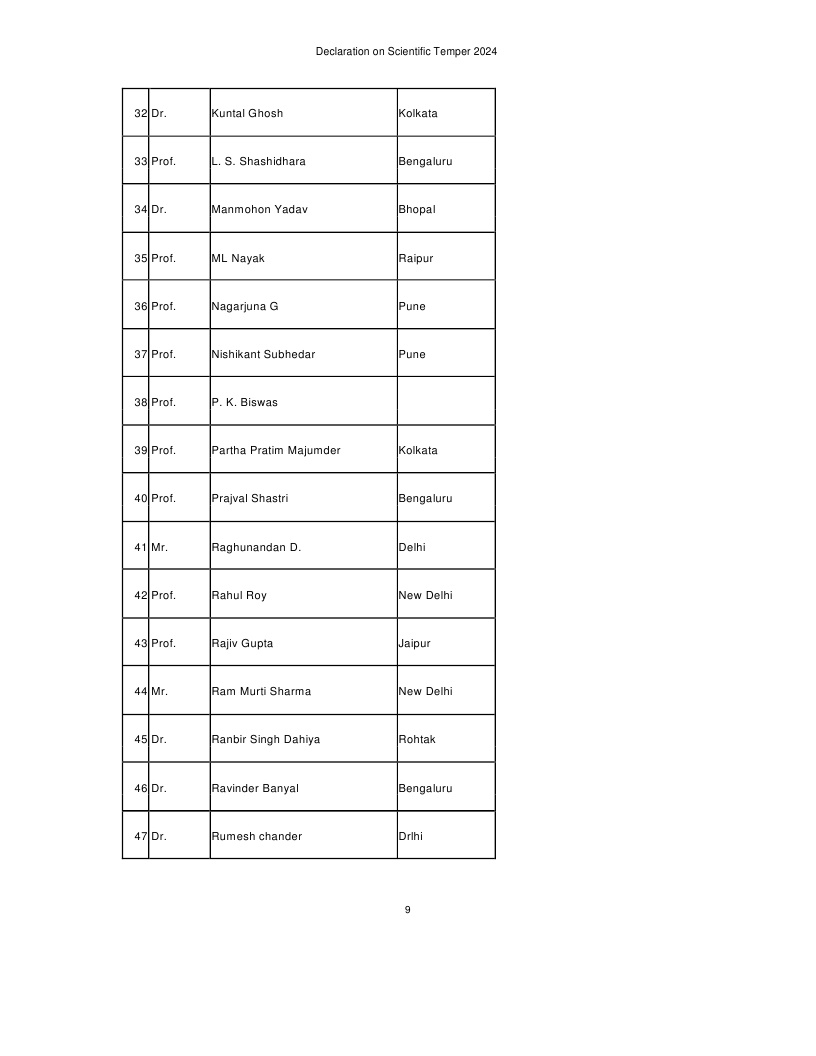
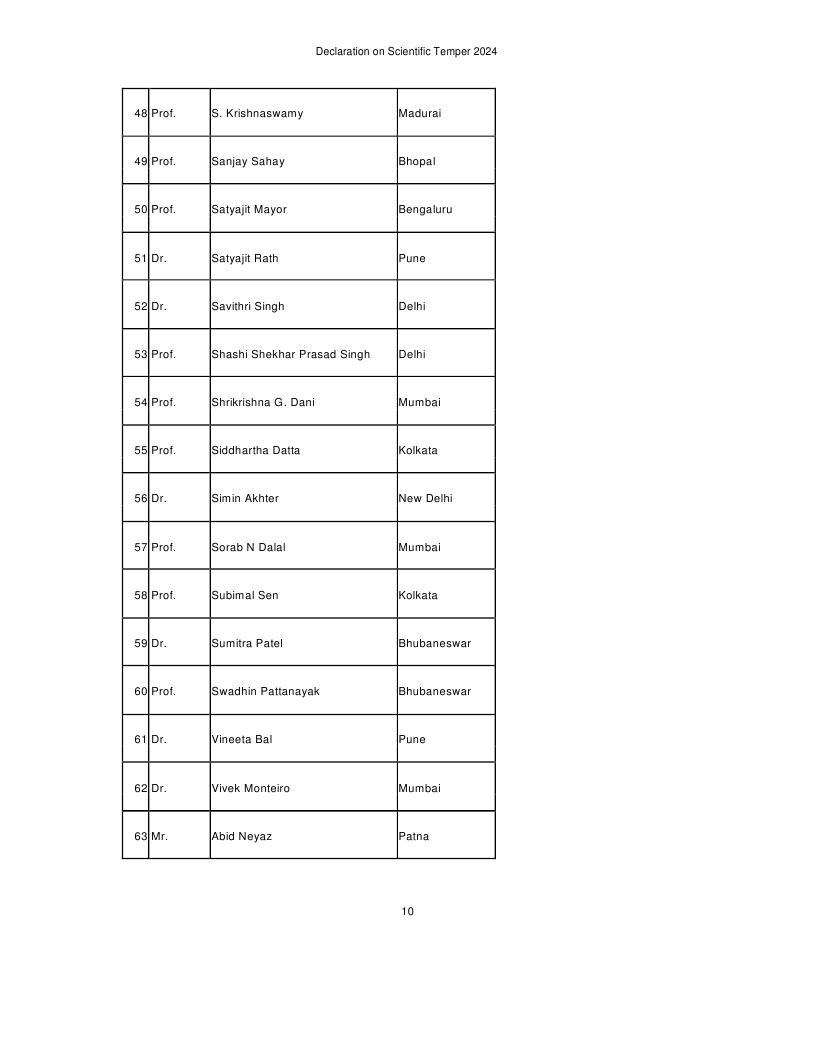
List of Signatories given below



For further information contact
Satyajit Rath 9868877399
Asha Mishra 9425302012
Arunabh Mishra 9831105979
Krishnaswamy 8012558638
Aniket Sule 9820273239
Resolution adopted by the AIPSN along with the “Statement on Scientific Temper Declaration”
in the “Campaign for scientific temper culmination program and National convention for declaration on scientific temper”
held on 28th Feb 2024 at Kolkata
Convinced that India that is Bharat grew for several centuries as Hindostan, and where the people of various religions chose to live together after becoming politically independent from the British Empire and experiencing the partition, is not a society of comparative and competitive religious fanaticism;
Certain that Hindostan is not the land of make-believe demands on Astha (the tradition of belief systems) alone, but that Hindostan is also the land of modern interpretations of religion;
Confident that Hindostan is the land of the rich tradition of syncretism (combining different traditions) and of seekers of the Universal Truths in religions, and that the people cherish civilizational heritage and celebrate the unity in diversity in food, dress and language on everyday basis;
Clear that Hindostan is the land where Nastiks and Astiks coexisted, materialistic philosophical traditions, for example, lokayata flourished, and the revolution of equality through Buddhism appealing to large sections of society took root, and where the traditions of rebellion and resistance grew through the teachings of Basava, Kabir, Nanak, Narayana Guru, Periyar and many more, promoted inclusiveness and syncretism of sufi and bhakti spiritual preachers;
Accepting that the people care for the legacy of the freedom movement, constitutional vision, national unity and integrity, and do not doubt that the majority is concerned about economic, ecological and social justice, and they continue to think about fundamental rights and directive principles of state policy enshrined in the Indian Constitution;
Recognizing that the people as bearers of historical knowledge, skills and culture, and as social carriers of agro-food diversity, culinary heritage, dietary selections, continue to enjoy variegated range of food, health and fitness practices, and they would be willing to stand up once again against the bearers of sectarian politics trying to take away their economic, social and political freedoms;
Recalling that the contributions to modern science & technology made by J C Bose, M Visvesvaraya, P C Ray, C V Raman, M N Saha, P C Mahalanobis, S N Bose, S.S. Sokhey, SS Bhatnagar, Homi Bhabha, Vikram Sarabhai, Satish Dhawan and by many others who challenged the colonial order in S&T, and the perspective and strategy of Scientific Policy Resolution (SPR, 1958) which cherished self-reliance and, embraced scientific approach to policymaking, the scientific and technological communities would not let the people suffer unreason and eliminate the space for pluralism and diversity from the world of higher education, science, technology and humanities;
Persuaded that as the post-independent India’s transformative impulses of self-reliance that accommodated the Gandhians, Nehruvians and Leftists to practice their own S&T heuristics for development in the parallel, gave a place to the ethos of scientific temper and humanism in the Indian Constitution, and in the National Curriculum Framework (2005) and in the Right to Education legislation (2008), the Indian S&T community and the people can be mobilized to defend these gains;
Knowing that the ecumenical (promoting unity among religions), cosmopolitan and modern traditions of scientific and technical practice have deep roots in India, the S&T community can be made to appreciate that the sources of ancient and medieval contributions to science involved multi-cultural interactions, and that the attempts to present mythology as history and fiction as science do not resonate well with the people, the vast majority of Indian people can be made to understand how the latest modern construction of the past traditions is to present an ideology that glosses over and hides the inequalities and exploitation based on caste, class, gender and community;
Recognising that as the people resisted Brahmanism and caste oppression in the ancient and medieval times, the latest attempts to cultivate and impose the irrational and unreasonable ideas on the Indian Women, Youth, Adivasis and Dalits can also be defeated among the people across North, South, East and West of India by mobilizing the people against the assault on scientific temper in the relevant spheres of school and higher education, scientific research and science popularisation;
Feeling alarmed at the Union Government’s blatant unconstitutional attempts to impose on the states the National Education Policy (NEP, 2020), that has the potential to damage irreparably the national character and destroy the secular and democratic contributions of Indian education, the Peoples’ Science Movements (PSMs) call upon the state governments to resist the efforts that sow the seeds of hatred and conformism deep into the mind of the young under the influence of the idea of Hindutava – a destructor of social progress and universal brotherhood/sisterhood, and rededicate themselves to developing quality education with public purposes of national importance
As PSMs,
We solemnly affirm our constitutional right to defend the integrity of Article 51 A(h), and to ensure that the investments in education, science, technology, humanities and arts are considerably enhanced and directed to work for the realization of the scientific temper/outlook[1], for the cultivation of linguistic and socio-cultural diversity, for the universally cherished message of love (‘Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’ – the world is one family’ ) and for the secular and socialist idea of India and for the reduction of inequalities;
We will contribute to the movements seeking economic, social and ecological justice, and work for the dignified livelihood for the Indian people as a whole through education and research, commit to redouble our own efforts for the promotion of progressive anti-imperialist nationalism, and to strengthen the role and contribution of Indian S&T institutions in the processes of decision making and evaluation of the socio-economic policies under implementation;
We continue with the work started by Dara Shikoh, Savitribai and Jyotriba Phule, Ramabai, Rabindranath Tagore, Nehru, Mahatma Gandhi, Periyar, Bhim Rao Ambedkar, EMS Namboodripad, Ashfaqullah, Bhagat Singh, Subhas Bose, Meghnath Saha, S.S Bhatnagar, Homi Bhabha, S.S. Sokhey, Vikram Sarabhai Husain Zaheer and many others who stood their ground and established the edifice of post-independence period modern S&T institutions, and helped the people to realize the idea of India and the legacy of progressive traditions of the freedom movement;
Mobilize the scientific community to stand up for academic freedom, and actively collaborate with the democratic movement and civil society to defend civil liberties and democratic rights, freedom of expression, organization, representation and struggle through constitutional means, and expose and isolate the forces supporting the babas spreading fatalism and unreason,
Collaborate and work with the rationalists, scholars, academics, scientists, technologists, social scientists, teachers of humanities and sciences, and professionals about the way forward for the realization of the above stated goals of social progress, propose policies, build institutions and establish a standing mechanism to pursue the challenge of cultivation of scientific temper, humanism and world peace.
[1] The term scientific temper is broadly defined as “a modest open-minded temper—a temper ever ready to welcome new light, new knowledge, new experiments, even when their results are unfavourable to preconceived opinions and long-cherished theories.
For further information contact
Satyajit Rath 9868877399
Asha Mishra 9425302012
Arunabh Mishra 9831105979
Krishnaswamy 8012558638